Linux-Basics-Complete-Course-With-Notes-Slides
DPKG and APT Package Managers
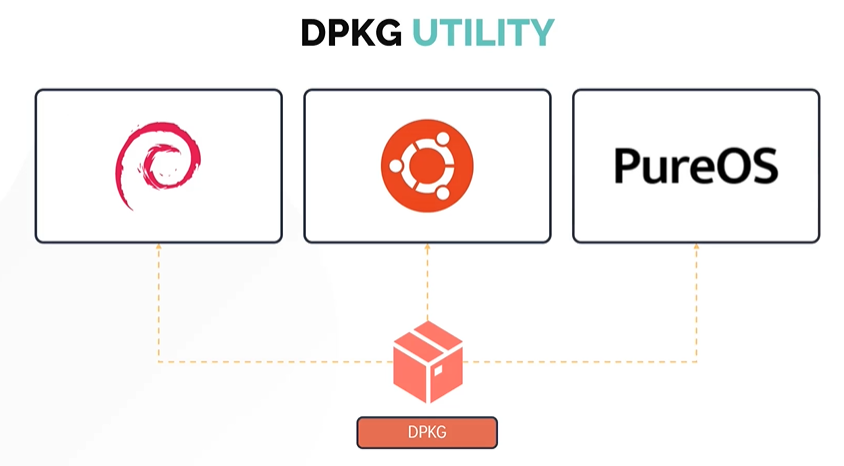
In this section, we will look at debian package managers for distributions like Ubuntu, Debian and PureOS.
- DPKG
- APT
DPKG Utility
- DPKG stands for Debian Package Manager
- It is a low level package manager
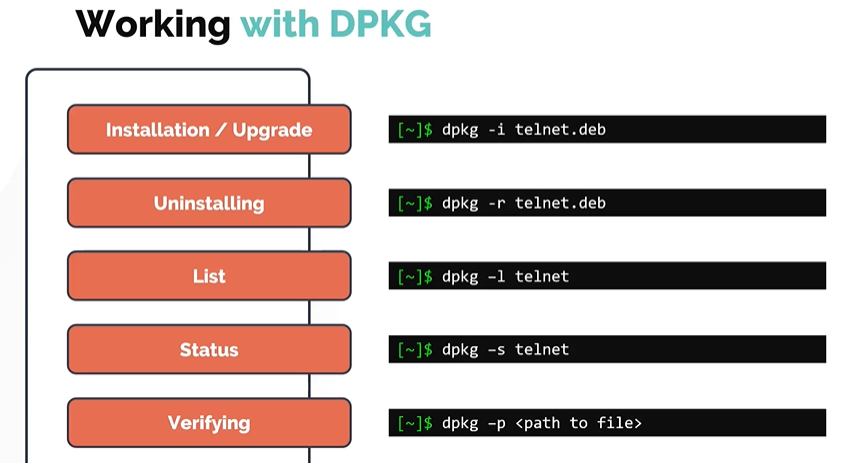
Working with DPKG
Similar to RPM, DPKG can be used for the below. The package extension is .deb.
- Installing
- Uninstalling
- Upgrade
- List
- Status
-
Verfiying
APT and APT-GET
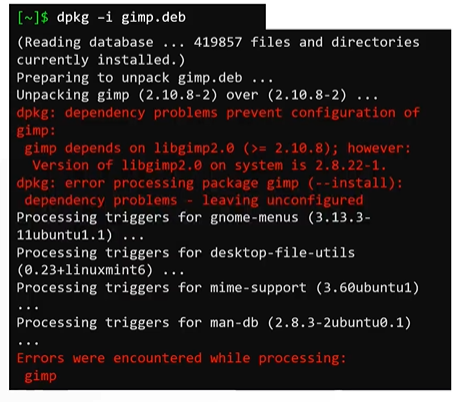
Similar to RPM, DPKG doesnt resolve the dependencies when it comes to package management.
-
Install may fail due to dependencies issues. This is the reason why we use higher level debian package managers such as
APTandAPT-GET. - Instead of relying on DPKG, you can install software along with its dependencies using
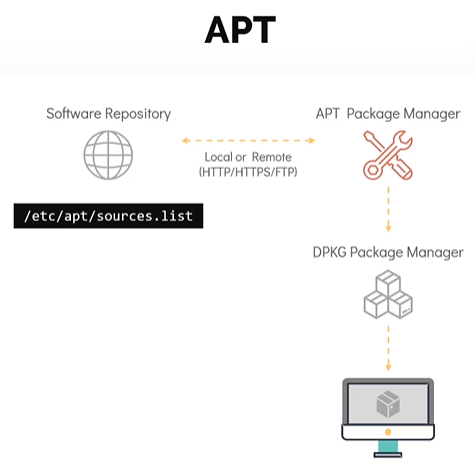
APTorAPT-GET. APTorAPT-GETalthough sounds similar, but they do not depend on each other.APTstands for advanced package managers, it is more user friendly and overall better tool compared toAPT-GET.$sudo apt install gimp $sudo apt-get install gimp- APT act as a frontend package manager that relies on DPKG utility. In similar to YUM, APT relies on software repository that contains packages that would eventually be installed on a system.
-
The software repository for APT is defined in
/etc/apt/sources.listfile.
Let us know see some common commands
To refresh a repository. Run apt update command.
$ sudo apt update
To install available upgrades of all packages currently installed on the system from the sources configured.
$ sudo apt upgrade
Another way to update the repository is to use apt edit-sources command. This opens up the /etc/apt/sources.list file in the text editor of your choice.
$ sudo apt edit-sources
To install the package
$ sudo apt install telnet
To remove the package
$ sudo apt remove telnet
To search or look for a package in the repository.
$ sudo apt search telnet
To list all the available packages
$ sudo apt list |grep telnet