Linux-Basics-Complete-Course-With-Notes-Slides
SYSTEMD Tools to Manage SYSTEMD service
In this lecture we will explore two major SYSTEMD tools:
- SYSTEMCTL
- JOURNALCTL
## SYSTEMCTL
- Systemctl is the main command used to manage services on a
SYSTEMDmanaged server. - It can be used to manage services such as
START/STOP/RESTART/RELOADas well asENABLE/DISABLEservices during the system boot. -
It is also used to
LIST AND MANAGE UNITSandLIST AND UPDATE TARGETS
Systemctl Commands
-
To start a service use the start command, for example to start a docker service use
systemctl start docker[~]$ systemctl start docker -
To stop a service use the stop command, for example to stop a docker service use
systemctl stop docker[~]$ systemctl stop docker -
To restart a service use the restart command, for example to restart a docker service use
systemctl restart dockerthis will stop and start again.[~]$ systemctl restart docker -
To reload a service use the reload command, for example to reload a docker service use
systemctl reload docker, this will reload all the configuration without interrupting the normal functionaltiy of the service[~]$ systemctl reload docker -
To enable a service and make it persistent accross reboots use the enable command, for example to enable a docker service use
systemctl enable docker[~]$ systemctl enable docker -
To disable a service at boot use the disable command, for example to disable a docker service use
systemctl disable dockercommand.[~]$ systemctl disable docker -
To know the status of the service use
systemctl status dockercommand. This command provided the state of the service. If running properly is should showactive (running)state as shown in screenshot below.[~]$ systemctl status docker -
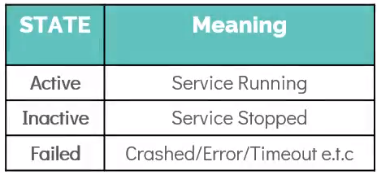
Besides
active (running)state there are few other state that you should be aware off. -
Running
systemctl daemon reloadcommand after making changes to service unit file reloads the system manager configuration and makes the systemd aware of the changes. -
To edit the service file use command
systemctl edit project-mercury.service --fullthis will open a text editor, you can make the changes and re-write the settings as needed, making changing this way applied immediately without running thesystemctl daemon reloadcommand[~]$ systemctl daemon-reload [~]$ systemctl edit project-mercury.service --full -
To see the current runlevel use
systemctl get-default[~]$ systemctl get default -
To change the runleve to a different target use
systemctl set-default multi-user.target[~]$ systemctl set-default multi-user.target -
To list all the units that systemd has loaded use
systemctl list-units --all, this lists all the unit which are active, inactive or anyother state.[~]$ systemctl list-units --all -
To list only active units use
systemctl list-unitscommand[~]$ systemctl list-units -
To view, and also locate a unit file use
systemctl catcommand. A comment line containing the path to the unit file is printed as the first line of output.[~]$ systemctl cat project-mercury.service
JOURNALCTL
- Journalctl is a command for quering/viewing logs collected by systemd.
- The systemd-journald service is responsible for systemd’s log collection, and it retrieves messages from the kernel systemd services, and other sources.
-
Very useful when you are troubleshooting issues with systemd services.

-
Using
journalctlcommands print all the log entries from oldest to the newest.[~]$ journalctl -
Using
journalctl -bcommand print all the logs from the current boot.[~]$ journalctl -b -
Using
journalctl -u docker.servicecommand print all the logs specific to the unit specified, for example docker in this case.[~]$ journalctl -u docker.service -
Using
journalctl -u docker.service --sincecommand print all the logs specific to the unit specified since the given time, for example docker in this case.[~]$ journalctl -u docker.service --since "2022-01-01 13:45:00"